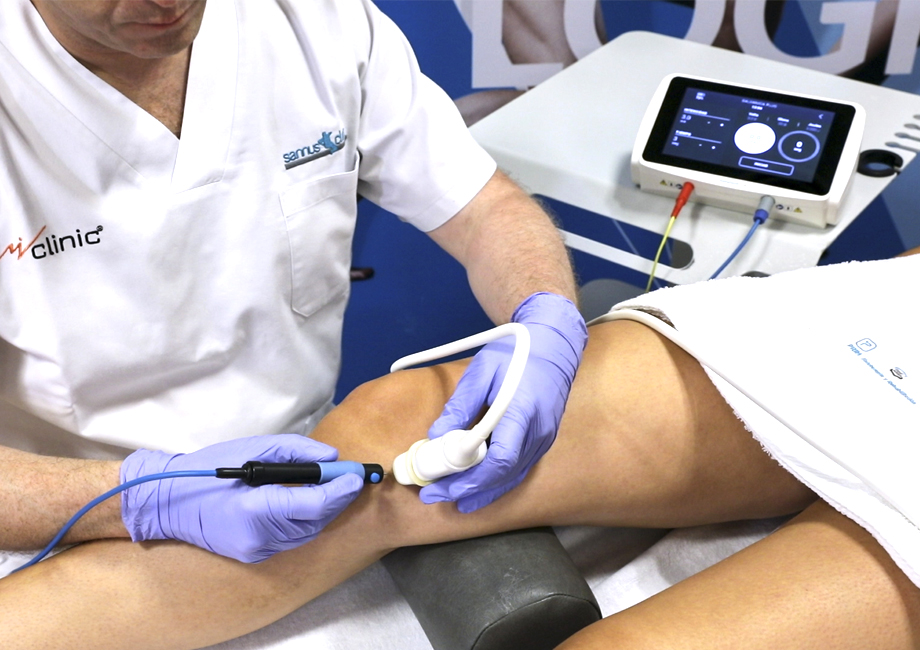
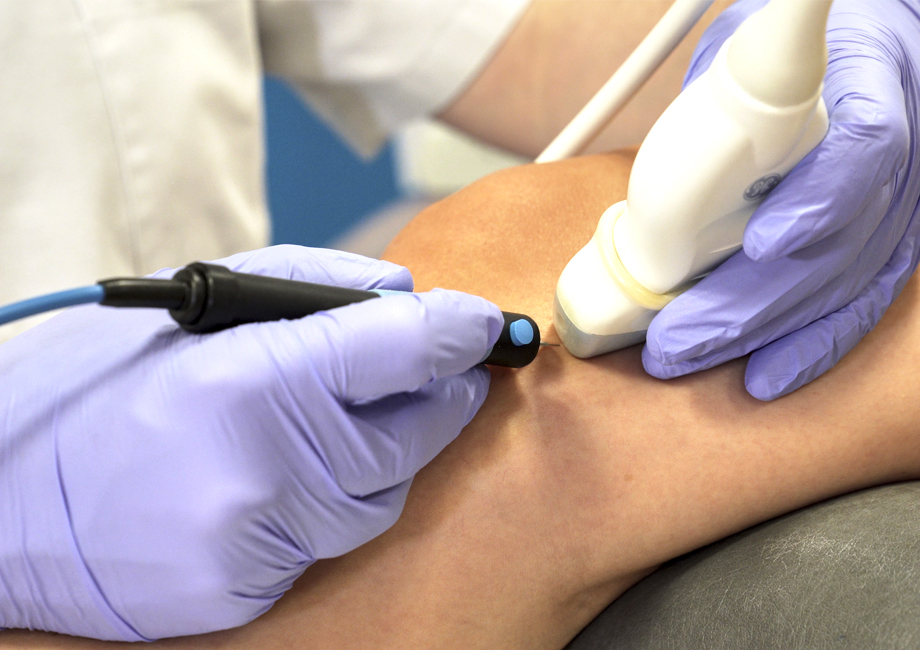
What is USGET (UltraSound-Guided Percutaneous Electrolysis technique) ?
Regenerative electrolysis is a form of percutaneous stimulation which has been developed in Spain to convey inside the tissues the currents which were already being applied transcutaneously through the Dry Needling technique, to amplify the effects of the current.
The galvanic current flows through an agopuncture needle triggering in turn an inflammatory reaction inside the tissue. This inflammatory reaction triggers a series of biological processes inside the body, which activate the production of collagen and promote the treatment of the pathology.
The aim of the inflammatory process is to change the status of the injury of the patient from chronic to acute. The needle works as a current transmitter and allows the operator to treat accurately both deep and superficial areas.
In which cases is USGET recommended?
USGET performed with galvanic current combines the diagnostic and the therapeutic moment in a single gesture, is minimally invasive and opens thus interesting new perspectives for the treatment of tendon pathologies, for which, as of today, there is no final protocol.
USGET is a technique more commonly employed on tissues with chronic impairments; it has shown good results on tendons in the chronic stage and can also be employed in case of old muscle injuries, to treat myofascial pain syndrome and trigger points.
The Physio Invasiva 2.0 device
Physio Invasiva 2.0 is a versatile device, comprising all the most efficient and innovative electrical currents in the field of percutaneous electrostimulation.
In addition to the galvanic current which allows to perform USGET safely and accurately, Physio Invasiva 2.0 also has other currents such as PES, PES 2.0, microcurrents and TENS, which, by acting on neuromodulation, have an antalgic effect and are optimal for performing anti-inflammatory treatments.
Additionally, the latter can be used independently or as a support to the treatment with the galvanic current to amplify its effect and reduce pain as much as possible.

